Introduction:
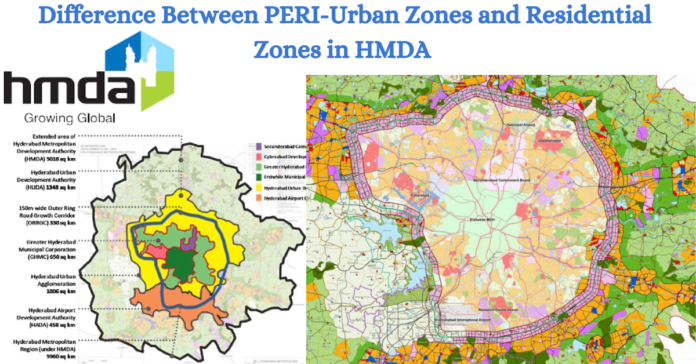
Hyderabad, one of India’s fastest-growing metropolitan cities, has undergone substantial urban expansion and development in recent years. To effectively manage this growth and ensure sustainable urbanization, the Hyderabad Metropolitan Development Authority (HMDA) has implemented a comprehensive zoning framework. Among the various zoning classifications, PERI-Urban Zones and Residential Zones play pivotal roles in shaping the city’s landscape.
1. Location and Definition:
PERI-Urban Zones: These are areas located on the outskirts of Hyderabad, serving as a transition between the densely populated urban core and the surrounding rural areas. They are characterized by a mix of urban and rural features, often experiencing rapid growth and development.
Residential Zones: These are specifically designated areas within the city or its suburbs that are primarily intended for housing and community development. Residential zones are integral to urban planning, ensuring organized growth and the creation of livable neighborhoods.
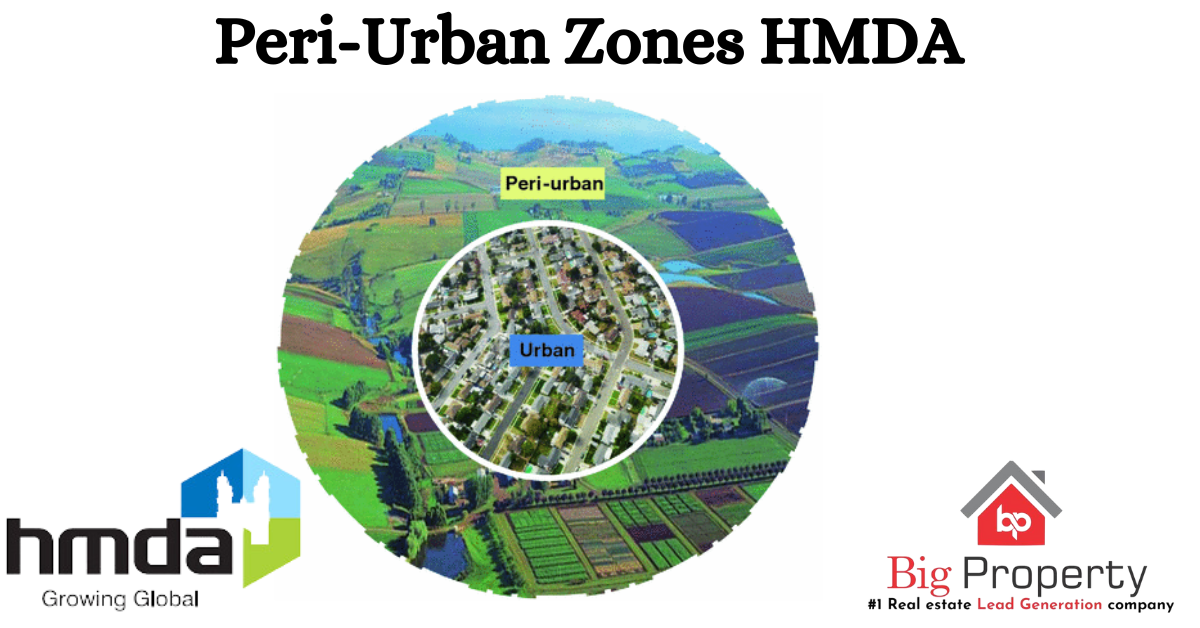
2. Land Use and Development:
PERI-Urban Zones: These zones often have mixed land uses, including residential, commercial, industrial, and agricultural activities. They are typically more versatile, allowing for a range of developments due to their proximity to urban and rural areas.
Residential Zones: The primary focus is on housing. Commercial and industrial activities are limited to maintain a peaceful, residential atmosphere. Residential zones have stricter regulations to ensure that the area remains conducive to living.
3. Infrastructure:
PERI-Urban Zones: These areas often witness significant infrastructure development, such as new roads, highways, and public transportation systems, to support their rapid growth. However, infrastructure in these zones can sometimes lag due to the pace of development.
Residential Zones: These zones are generally equipped with essential infrastructure, including well-maintained roads, reliable water supply, and proper sanitation facilities, as they are planned for long-term residential use.
Also Read: What About PERI-Urban Zones in Hyderabad Metropolitan Development Authority (HMDA)
4. Growth Potential:
PERI-Urban Zones: Due to their proximity to the city center and lower land costs, PERI-Urban Zones have high growth potential for both residential and commercial development. These areas are often attractive to investors and developers looking for emerging markets.
Residential Zones: Growth in residential zones is more controlled and planned, focusing on maintaining the area’s character. While they can experience growth, it is typically more stable and gradual compared to the rapid expansion seen in PERI-Urban Zones.
5. Zoning Regulations:
PERI-Urban Zones: Zoning in these areas is more flexible, allowing for a mix of uses. The regulations are designed to accommodate the diverse needs of a transitioning area, balancing urban expansion with rural preservation.
Residential Zones: These zones are strictly regulated to ensure that the primary focus remains on housing. Height restrictions, land use limitations, and other zoning laws are enforced to maintain the residential nature of the area.
6. Challenges and Opportunities:
PERI-Urban Zones: The rapid urbanization in these zones can lead to challenges such as traffic congestion, pollution, and strain on resources. However, they also offer significant opportunities for growth and development.
Residential Zones: The main challenges include ensuring adequate infrastructure and services as the population grows. However, these zones offer stable, organized growth, making them desirable for long-term residential planning.
7. Real Estate Prices and Demand:
PERI-Urban Zones: Real estate prices in these areas are generally lower compared to central urban areas, making them attractive for new investments. However, as development progresses, prices tend to rise rapidly, reflecting the growing demand for residential, commercial, and industrial spaces.
Residential Zones: Real estate in established residential zones typically has higher prices due to the availability of established infrastructure and amenities. Demand in these areas is usually steady, driven by the desire for stable and secure living environments.
8. Social and Cultural Landscape:
PERI-Urban Zones: These areas often experience a blend of urban and rural lifestyles. The population in PERI-Urban Zones is typically diverse, with a mix of long-term rural residents and new urban settlers. This blend can lead to cultural exchange but also to challenges in integrating different social norms and lifestyles.
Residential Zones: The social landscape in residential zones is more homogenous, often characterized by a community-oriented environment. These areas are designed to foster community interaction, with schools, parks, and recreational facilities playing a central role.
Also Read: What About Residential Zones in Hyderabad Metropolitan Development Authority (HMDA)
9. Environmental Impact:
PERI-Urban Zones: Rapid development in PERI-Urban Zones can lead to significant environmental changes, including deforestation, loss of agricultural land, and increased pollution. These zones are at risk of facing environmental degradation if sustainable practices are not adopted during development.
Residential Zones: Environmental considerations in residential zones are often integrated into urban planning, with green spaces, parks, and sustainable infrastructure being key features. However, increased population density in these zones can also lead to environmental stress if not managed properly.
10. Examples:
PERI-Urban Zones: Examples include areas like Kondapur, Gachibowli, Kukatpally, and Madhapur, which have seen rapid development due to their strategic location on the outskirts of Hyderabad.
Residential Zones: Examples include R1, R2, R3, and R4 zones within Hyderabad, each with specific regulations and characteristics designed to support different types of residential development.
The differences between PERI-Urban Zones and Residential Zones in Hyderabad based on the provided content:
| Feature | PERI-Urban Zones | Residential Zones |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Outskirts and transitional areas between rural and urban | Established within the urban core |
| Infrastructure | Developing, often lacking in basic utilities | Well-developed, with established infrastructure |
| Land Use | Mixed-use, including agriculture, residential, and industrial | Primarily residential with regulated commercial activities |
| Planning & Zoning Regulations | Flexible, evolving with rapid development | Stringent, focused on maintaining residential character |
| Development Potential | High, with opportunities for new investments | Stable, focused on maintaining quality of life |
| Population | Rapidly growing, diverse demographic | Steady, more homogenous demographic |
| Real Estate Prices & Demand | Lower prices with potential for rapid increase | Higher prices, steady demand |
| Social & Cultural Landscape | Lower prices with the potential for rapid increase | Community-oriented, homogenous |
| Environmental Impact | Risk of environmental degradation with development | Integrated environmental considerations |
| Transportation & Connectivity | Developing infrastructure, reliance on private vehicles | Established public transport networks |
| Urban Planning & Governance | Flexible planning, challenges in governance | Stringent planning, stable governance |
| Economic Activities | Diverse, with opportunities in agriculture, manufacturing | The blend of rural and urban lifestyles |
| Future Development Prospects | Potential for transformation into urban areas | Focused on enhancing quality of life |
| Land Acquisition & Conversion | Complex due to mixed land use | Straightforward, with focus on residential development |
| Role in City Expansion | Key frontier for urban growth | Provides stable living spaces within the city |
| Community Facilities & Services | Developing, with challenges in access | Well-equipped with essential services |
| Population Density | Aimed at maintaining the quality of life and regulating land use | Higher, with compact housing developments |
| Government Initiatives & Policies | Focused on promoting balanced development | Service-oriented, supporting the local population |
| Examples in Hyderabad | Shamirpet, Maheshwaram, Kadthal | Jubilee Hills, Banjara Hills, Kukatpally |
Also Read: What to Check Before Buying a Plot in an HMDA Project?
Conclusion:
The growth and development of Hyderabad have been significantly influenced by the strategic planning of its PERI-Urban and Residential Zones. While PERI-Urban Zones serve as dynamic areas of transition between urban and rural settings, offering immense growth potential, Residential Zones ensure organized, stable environments for long-term living. Both zones are essential to the city’s urban landscape, balancing rapid expansion with sustainable living. Understanding their unique characteristics and challenges is crucial for investors, developers, and residents alike as they navigate Hyderabad’s evolving real estate market.
Frequently Asked Questions:
A PERI-Urban Zone is an area on the outskirts of Hyderabad that transitions between urban and rural areas, featuring a mix of residential, commercial, industrial, and agricultural activities.
Residential Zones are designated primarily for housing and community development, with stricter regulations to maintain a peaceful living environment, whereas PERI-Urban Zones allow for more diverse land uses.
PERI-Urban Zones have high growth potential due to their proximity to the city center and lower land costs, attracting investors and developers.
Yes, real estate prices in established Residential Zones are generally higher due to the availability of infrastructure and amenities, making them desirable for stable living.
Rapid development in PERI-Urban Zones can lead to environmental issues like deforestation and pollution, requiring sustainable practices to mitigate these impacts.
Suggested Articles:
What About PERI-Urban Zones in Hyderabad Metropolitan Development Authority (HMDA)
What About Residential Zones in Hyderabad Metropolitan Development Authority (HMDA)
Why Maheshwaram Real Estate Emerging Urban Hub? Reasons