Are You Want to Know More Information on the GST? Then, you must read this blog post. Let’s get into detail about the latest blog post – GST: 2023 – A Game Changer for India’s Economy.
1) Introduction
Goods and Services Tax (GST) is an indirect tax system that has revolutionized the Indian taxation system. GST, which went into effect on July 1st, 2017, is a comprehensive tax imposed on the production, sale, and consumption of goods and services throughout the nation. GST has replaced the previous system of indirect taxes, including VAT, Service Tax, and Central Excise Duty, among others. This blog will provide a comprehensive overview of GST, its features, benefits, challenges, and impact on the Indian economy.

2) What is GST?
GST is a tax that India imposes on the exchange of goods and services. It is a destination-based tax that is levied at every stage of the value chain. The state and central government levy GST on the value added at each stage of the production and distribution of goods and services, and they collect the tax while sharing the revenue generated between them.
3) What Is GST Portal?
The GST Portal is a tool or area that taxpayers can use to carry out several tax-related tasks. The foundation of the GST Portal, which serves as a conduit for communication between taxpayers and the government, is the Goods and Service Tax Network (GSTN).
4) Features of GST
Following are some of the key aspects of GST:
One nation, one tax: GST has replaced the complex indirect tax structure with a simple and uniform tax system that is applicable throughout the country.
Dual structure: Because of its dual structure, GST is imposed by both the federal and state governments.
Destination-based tax: GST is a destination-based tax, which means that it is levied at the point of consumption.
Input tax credit: One of the key features of GST is that it allows businesses to claim input tax credit, which means that the tax paid on inputs can be offset against the tax liability on the final product.
Threshold limit: GST has a threshold limit, which means that small businesses with an annual turnover of GST is not due on purchases beyond Rs. 40 lakh.
5) Benefits of GST
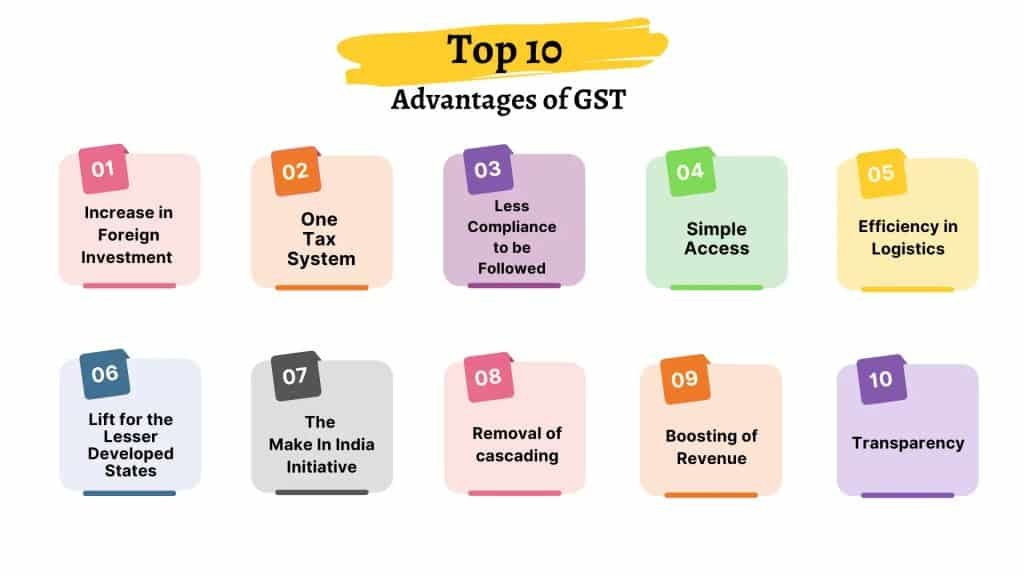
GST has some benefits, which are as follows:
Simplified tax structure:
GST replaced various taxes with a single tax, simplifying the tax structure.
Boost to the economy:
GST has helped in boosting the economy by reducing the cost of goods and services and increasing their demand.
Ease of doing business:
GST has made it easier for businesses to operate by simplifying the tax structure and providing a single tax registration.
Elimination of tax cascading:
GST has eliminated the tax cascading effect by allowing input tax credits, which has reduced the tax burden on businesses.
Increased tax compliance:
GST has increased tax compliance by providing a transparent and easy-to-understand tax system.
6) Challenges of GST
Despite its benefits, GST has also faced some challenges, which are as follows:
Technical glitches: The implementation of GST has been marred by technical glitches, which have affected the compliance and filing process.
Increased compliance burden: GST has increased the compliance burden on small businesses, which has impacted their profitability.
Inadequate IT infrastructure: The IT infrastructure required for GST implementation was inadequate, which led to technical glitches and delayed implementation.
Lack of clarity: There is still some lack of clarity around the GST laws and regulations, which has led to confusion and compliance issues.
Multiple Tax Rates: GST has multiple tax rates which have made it complex for businesses to comply with tax regulations. It has also led to confusion among consumers regarding the tax rates on different goods and services.
Compliance Burden: GST replaced various taxes with a single tax, simplifying the tax structure. Businesses need to file multiple returns and comply with various tax regulations, which has increased the cost of compliance.
7) GST’s effects on India’s economy
GST has had a significant impact on the Indian economy, some of which are as follows:
Boost to GDP: GST has helped in increasing the GDP growth rate by reducing the cost of goods and services and increasing their demand.
Increase in tax revenues: GST has led to an increase in tax revenues for the government, which has helped in reducing the fiscal deficit.
Simplified tax structure: GST has simplified the tax structure, which has made it easier for businesses to operate and for the government to administer the tax system.
8) GST Slabs
GST has four different tax slabs, which are as follows:

0% GST: This slab is applicable to goods or services that are exempted from GST. Some of the goods and services that fall under this slab are fresh fruits and vegetables, milk, curd, jaggery, unprocessed cereals, etc.
5% GST: This slab is applicable to goods or services that are of essential nature, such as basic groceries, tea, coffee, edible oils, etc.
12% GST: This slab is applicable to goods or services that fall under the category of standard goods, such as computers, mobile phones, processed food, etc.
18% and 28% GST: These slabs are applicable to goods or services that fall under the category of luxury goods or sin goods, such as tobacco products, aerated drinks, air conditioners, etc.
Conclusion
GST is a comprehensive tax system that has simplified the tax structure and made it easier for businesses to comply with tax regulations. It has brought about a uniform tax structure throughout the country and has eliminated the cascading effect of taxes. GST has boosted the GDP of the country and has reduced the cost of goods and services for consumers.
Also, Read Our Latest Blog Posts:
- Do You Know 13 Myths About HMDA Master Plan?
- Why Must Visit 15 Places in Hyderabad?
- Do You Know-BEST 10 PLACES TO VISIT IN WARANGAL
- Gold vs Real Estate: Which Is The Better & Smart Investment?
- Which House Facing Direction is Better to Live?
- 8 Helpful Advantages& Disadvantages – Investing in Hyderabad RealEstate
Frequently Asked Questions
A: The Full Form GST is Goods and Service Tax.
A: GST has 4 different slabs.
A: The 4 different slabs in GST are 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%.


